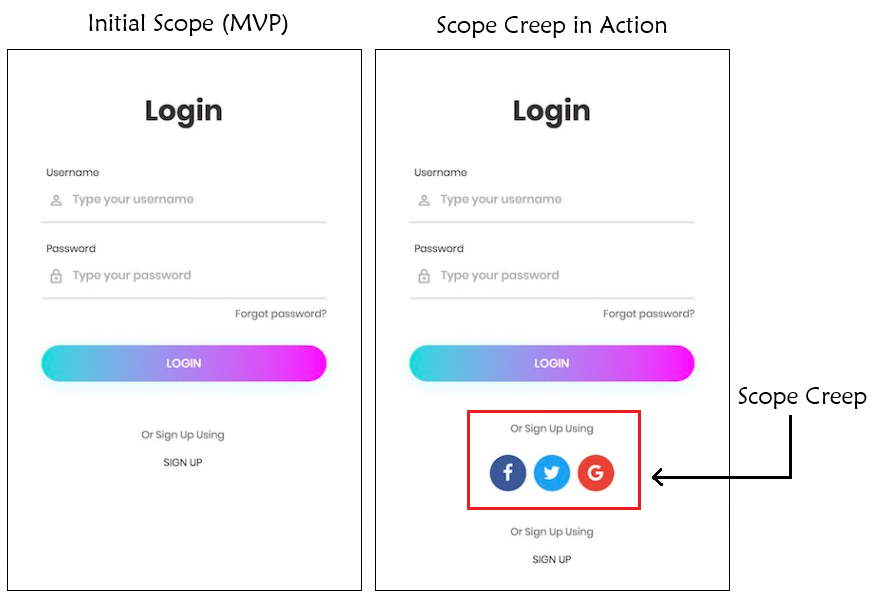
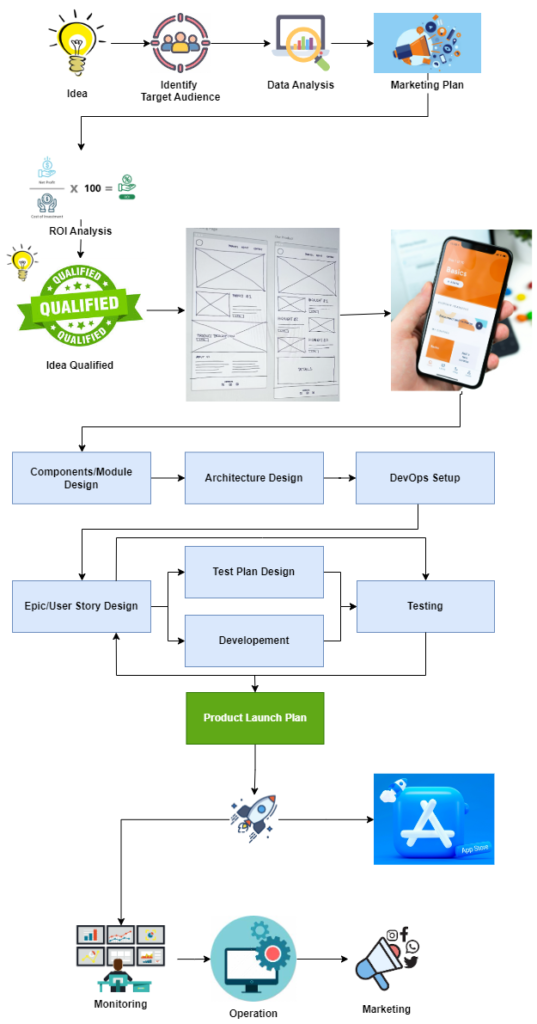
In the fast-paced world of technology, developing a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) product is akin to navigating a complex maze. The journey from a mere idea to a fully functional product involves multiple stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets the market demands and user expectations. The below image provides a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the key stages in the SaaS product development process. Let’s delve into each step to understand how to transform an idea into a successful SaaS product.
1. Ideation and Market Research
Idea: Every successful product starts with an idea. This initial spark is the foundation upon which the entire project is built. It’s essential to clearly define the problem your product will solve and envision the solution.
Identify Target Audience: Once the idea is formed, the next step is to identify the target audience. Understanding who will benefit from your product is crucial for tailoring features and functionalities to meet their needs.
Data Analysis: With a defined target audience, data analysis comes into play. This involves researching market trends, competitor products, and user behavior to gather insights that will shape your product development strategy.
Marketing Plan: Based on the data analysis, develop a marketing plan. This plan should outline how you will position your product in the market, the channels you will use for promotion, and the strategies for attracting and retaining customers.
2. Validation and Prototyping
ROI Analysis: Before proceeding, conduct a Return on Investment (ROI) analysis to ensure the idea is financially viable. This step involves evaluating the potential profitability and long-term sustainability of the product.
Idea Qualified: Once the idea passes the ROI analysis, it is considered qualified for further development. This qualification is a green light to move forward with more detailed planning and design.
Wireframes: Create wireframes to visualize the product’s structure and layout. Wireframes serve as a blueprint, illustrating the skeletal framework of the product, including the placement of elements and navigation flow.
UI/UX – Mockups: Based on the wireframes, develop detailed UI/UX mockups. These mockups provide a more refined and realistic representation of the product’s appearance and user experience, allowing for adjustments and improvements before development begins.
3. Detailed Planning and Design
Components/Module Design: With a clear vision of the product’s design, focus on the components and modules. This involves defining the individual parts that will make up the product, ensuring each is designed to perform its specific function effectively.
Architecture Design: Develop the product’s architecture, outlining the overall structure and how different components will interact. A well-designed architecture ensures scalability, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
DevOps Setup: Establish the DevOps environment to streamline development, testing, and deployment processes. A robust DevOps setup facilitates continuous integration and delivery, ensuring faster and more reliable product releases.
4. Development and Testing
Epic/User Story Design: Break down the product development into epics and user stories. This agile approach allows for manageable chunks of work, ensuring focused development and incremental progress.
Test Plan Design: Design a comprehensive test plan to ensure the product meets all quality standards. This plan should cover various testing methods, including unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance tests.
Development: With everything in place, the development phase begins. This is where the actual coding happens, translating the design and plans into a working product.
Testing: Concurrent with development, rigorous testing is conducted to identify and fix bugs, ensuring the product functions as intended and provides a seamless user experience.
5. Launch and Post-Launch Activities
Product Launch Plan: Prepare a detailed product launch plan. This plan should cover the launch date, promotional activities, and support strategies to ensure a smooth introduction of the product to the market.
Monitoring: Post-launch, continuous monitoring is essential to track the product’s performance, user feedback, and any issues that arise. Monitoring helps in making informed decisions for future updates and improvements.
Operation: Ensure smooth operation by maintaining the product, resolving technical issues, and updating features as needed. A well-maintained product keeps users satisfied and engaged.
Marketing: Continue with marketing efforts to attract new users and retain existing ones. Effective marketing strategies help in scaling the product and expanding its reach in the market.
Conclusion
Developing a SaaS product is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement. By following this comprehensive roadmap, you can navigate the complexities of product development and bring a successful SaaS product to market. Each step, from ideation to post-launch activities, plays a vital role in ensuring the product not only meets but exceeds user expectations, paving the way for long-term success.